Understanding the SDLC allows testers to anticipate risks and integrate quality at every stage rather than just finding bugs at the end. This alignment ensures that testing remains efficient, purposeful, and fully synced with the project’s evolving goals.
Waterfall Model
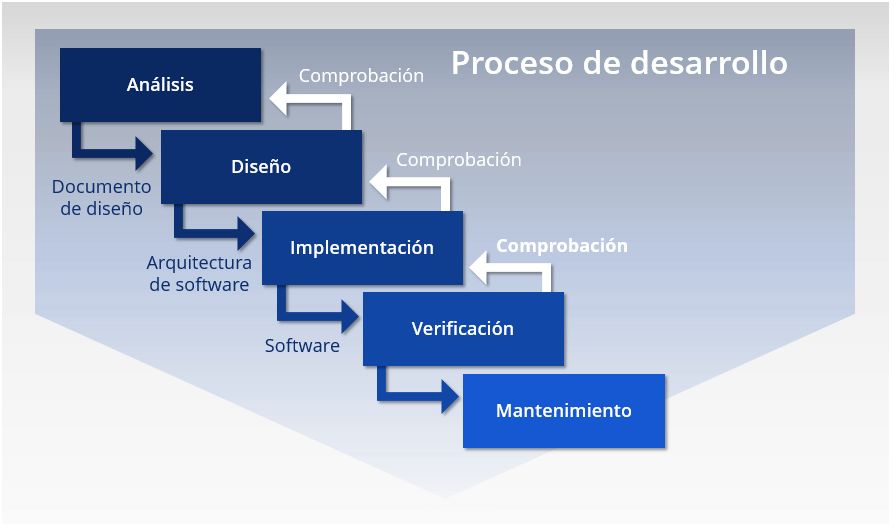
Disadvantages of the Waterfall Model
- It does not allow for changes in requirements.
- A functional product is not obtained until almost the end of the project.
- Sometimes, flaws are only detected at the end of the development process.
- The end-user does not participate in the production process until programming is finished.
Agile Development Methodologies
“SCRUM” Development Model

What is SCRUM?
SCRUM is a framework within agile software development that facilitates collaborative work in teams. It is based on the continuous application of good practices, defined roles (like Scrum Master, Product Owner, and Development Team), regular events (like sprints, daily meetings, reviews, and retrospectives), and artifacts that help achieve the best possible project outcome.
Advantages of Scrum
- Flexibility and adaptation to a changing market.
- Early results in short iterations.
- Obtaining a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) in early stages.
- Quick and accurate feedback thanks to continuous collaboration.
- Realistic project delivery date, based on planned sprints.
- Rapid team learning through retrospectives and continuous improvement.
- Autonomy and responsibility in a self-organized environment.
Roles in SCRUM
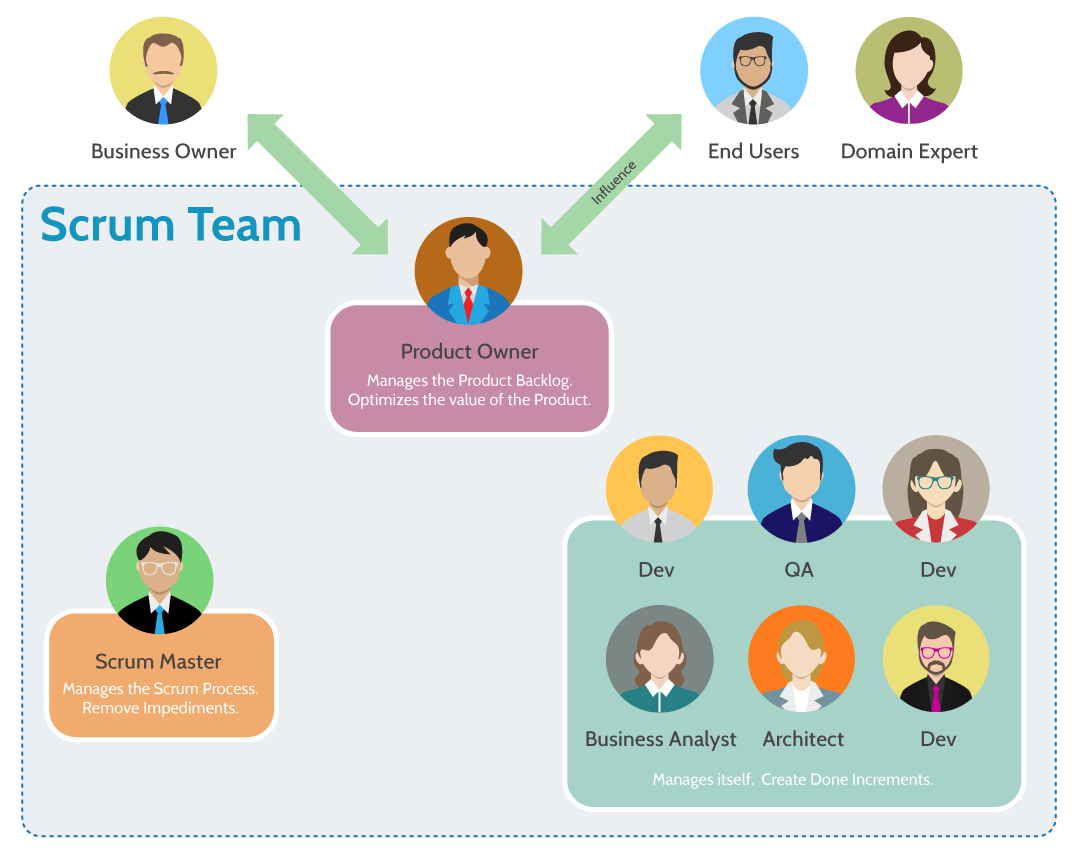
-
Scrum Master:
- An expert in the Scrum methodology.
- Facilitates the team’s work and removes impediments.
- Is not a Project Manager (PM), but a guide for the process.
-
Product Owner (PO):
- Represents the voice of the customer or the business.
- Defines priorities and manages the Product Backlog.
- Decides what should be developed and in what order.
-
Development Team:
- Cross-functional, includes roles such as:
- Developers (Devs).
- Business/Requirements Analysts (BAs).
- Testers/Quality Assurance (QA).
- Architects.
- Responsible for delivering functional increments in each Sprint.
- Cross-functional, includes roles such as:
SCRUM Events
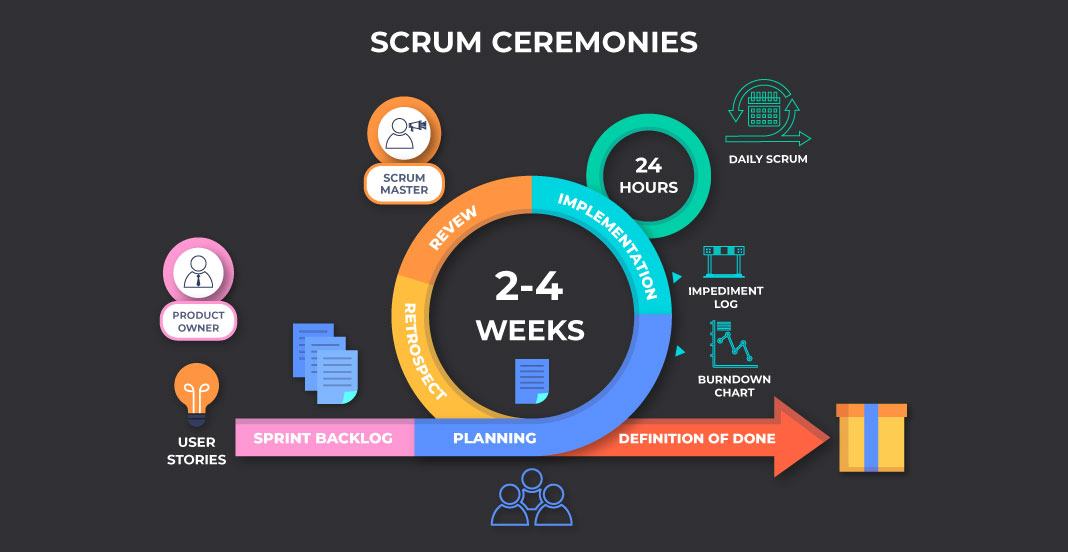
Sprint
The heart of SCRUM is the Sprint, and a Sprint is a period of time (cycle or iteration)—it can be 2 or 4 weeks—and during that time, several meetings (events) will be held. What are those meetings?
-
Sprint Planning: This is the first meeting held at the beginning of the sprint, used to select the items that will be worked on and how they will be done.
-
Daily Meeting (Daily): This is a 15-minute daily meeting where each member of the Development Team gives an update on what they are doing, as well as any impediments they have.
-
Sprint Review: This is a meeting that occurs at the end of the sprint where the PO and the team present the finished product increment to the users (stakeholders) for their inspection and adaptation.
-
Retrospective: A meeting that occurs at the end of the sprint where a reflection on the sprint is done, and opportunities for improvement for the next sprint are discussed.